How to Secure WordPress Files Using cPanel Settings
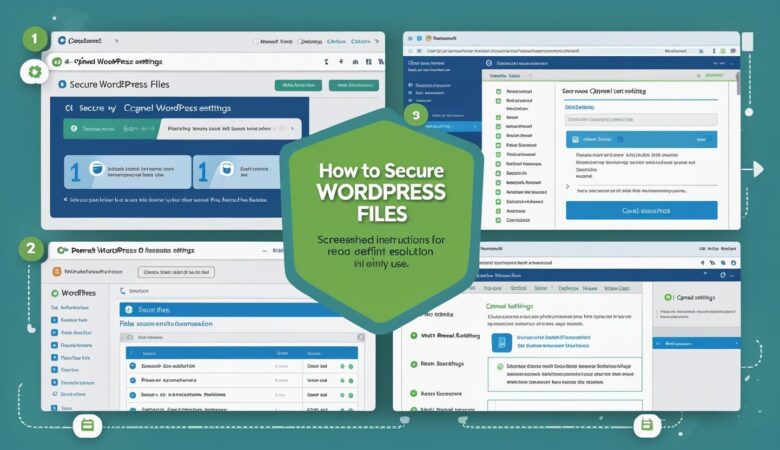
May 26, 2025How to Secure WordPress Files Using cPanel Settings Keeping your WordPress files secure is essential to protect your website from hackers, malware, and unauthorized access. In this guide, we’ll show you how to use cPanel tools to lock down your WordPress files and improve your site’s overall security. Why File Security Matters in WordPress WordPress websites are frequent targets for cyberattacks. By securing core files such as wp-config.php and directories like wp-content, you reduce the risk of data breaches, defacement, or site takeover. Step 1: Log In to Your cPanel Account Access your cPanel dashboard by visiting https://yourdomain.com/cpanel and logging in with your hosting credentials. Step 2: Use File Manager to Set Correct File Permissions Navigate to File Manager under the Files section. Go to the root directory of your WordPress installation (usually public_html). Right-click important files like wp-config.php and select Permissions. Set file permissions as follows: wp-config.php – 400 or 440 Other PHP files – 644 Folders – 755 Click Change Permissions. Step 3: Protect wp-config.php Using .htaccess This file contains your database credentials and must be kept secure. You can restrict access via .htaccess: In File Manager, open the public_html folder. Find and edit the .htaccess file. If it’s not visible, enable “Show Hidden Files”. Add the following code at the bottom of the file: # Protect wp-config.php <files wp-config.php> order allow,deny deny from all </files> Save and close the file. Step 4: Disable Directory Browsing Prevent visitors from browsing your website directories by adding this line to your .htaccess file: Options -Indexes Step 5: Password-Protect wp-admin Directory Add an extra layer of security to your admin area: In cPanel, go to Directory Privacy (or Password Protect Directories). Navigate to /public_html/wp-admin. Click Edit, then check “Password protect this directory.” Set a name and create a username and password. Step 6: Disable PHP Execution in wp-content/uploads Hackers often target this directory to upload malicious PHP files. To prevent this: In File Manager, go to /wp-content/uploads. Click + File to create a new file named .htaccess. Add the following code: <Files *.php> deny from all </Files> Save and close the file. Step 7: Monitor and Update Regularly Keep WordPress, plugins, and themes up to date. Use security plugins like Wordfence or iThemes Security. Regularly scan your site for malware using cPanel’s tools or external scanners. Securing your WordPress files via cPanel is a critical step in keeping your website safe from threats. With a few configuration changes and good maintenance habits, you can significantly reduce the risk of attacks.